Introduction
Movement is a community-first blockchain providing the highest possible TPS through Move, instant finality, native day-zero access to mass liquidity, and modular customizations.
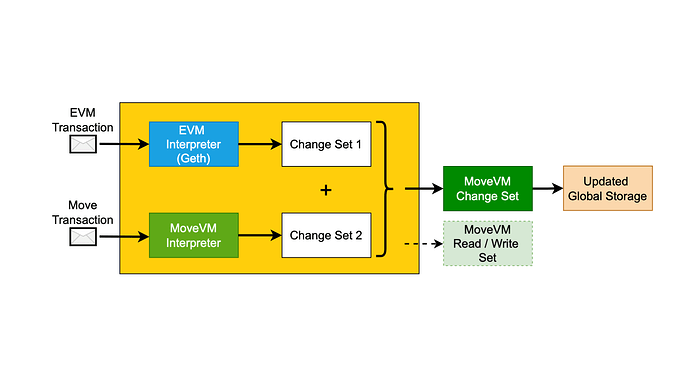
It will support Aptos Move, Sui Move, and also our embedded EVM interpreter MEVM—empowering both Sui, Aptos, and EVM users to use the L2.
Movement Staking
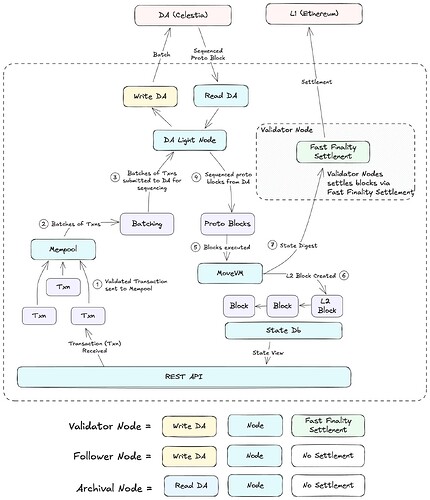
The Fast Finality Settlement Module is designed to provide fast confirmations and settlement for transactions. By utilizing a network of validators who stake assets and attest to the correctness of state transitions, this module ensures crypto-economic security and reduces latency. The validators combine the security benefits of staking with the efficiency of rapid transaction finality.
The Fast Finality Settlement includes Postconfirmations, see this blog (on-L1) and L2-confirmations (off-L1).
Security Mechanism
- Ethereum Settlement: Validators stake assets to provide economic security, ensuring significant financial interest in network integrity.
- ZK and Optimistic Rollups: ZK-rollups offer security through validity proofs, while optimistic rollups rely on challenge periods for dispute resolution. Both methods have higher latency and computational costs.
- Fast-Finality Chains: Offer fast-finality and high economic security without extensive proof generation or challenge periods, reducing latency and improving user experience compared to ZK and optimistic rollups.
Comparison with ZK and optimistic rollups
- Fast-Finality chains do not require expensive proof generation equipment, unlike ZK-rollups.
- Fast-Finality chains provide significantly reduced latency compared to both optimistic and ZK-rollups, with finality settlement in seconds.
- Fast finality is crucial for interoperability and atomic cross-chain transactions, making fast-finality chains an ideal solution for many applications.
Validator nodes check against the postconfirmed state root on L1 to increase their security and reduce the risk of providing wrong state updates to users. Initially - with the training wheels in place - a specialized node, called Core-Validator, is responsible for updating the state on L1.
As the training wheels are removed the network will move to a decentralized model where validators will be able to attest to the correctness of state transitions, and a supermajority of validators will be required to advance the state roots on L1.
LSaaS and rMOVE: Accelerating Movement Staking
StaFi’s development efforts in the LST domain are focused on two key areas:
- LSaaS Integration with Movement LSD Stack: Movement LST developers can quickly deploy a Movement LST with minimal development and configuration, leveraging StaFi’s robust LSaaS framework.
- rMOVE: Users can deposit MOVE tokens on the StaFi Protocol without any limitations based on their capacity. The deposited MOVE is then staked by StaFi’s staking contract, which autonomously selects the optimal sequencers to generate and maximize staking yields. Users who deposit MOVE on StaFi will receive an equivalent amount of rMOVE (rToken StaFi equivalent) to the value they staked. rMOVE is an rebaseable token, allowing users to freely trade rMOVE or provide liquidity (LP) to earn additional yield. This additional yield can be staked alongside reputable DEX partners on the Movement ecosystem.
Why Choose Movement
Movement is a next-generation high-performance Layer 1 blockchain that has gained significant attention in both capital and user markets. Supporting Movement with LSaaS can help increase market visibility. Additionally, Movement is currently in its mainnet phase, and establishing official contact with the Movement team will be a key focus going forward.